Our Research Projects
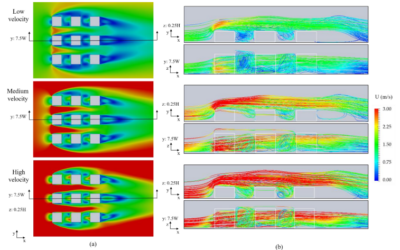
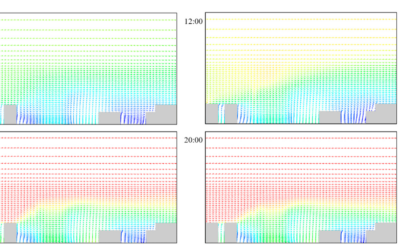
Systematic analysis of air pollution and urban ventilation
Seed Capital No. 074-2021, funded by SENACYT.
To evaluate the efficiency of urban ventilation to reduce air pollution under different urban parameters.
Modeling and Simulation of Urban Outdoor Air Pollution in Panama City
APY-NI-2021-61, funded by SENACYT.
Model and simulate the dispersion of atmospheric pollutants in critical areas of the city using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) considering the influence of fixed and mobile emissions, meteorology and local geometric configuration to estimate outdoor ambient air pollution levels in the province of Panama, Republic of Panama.
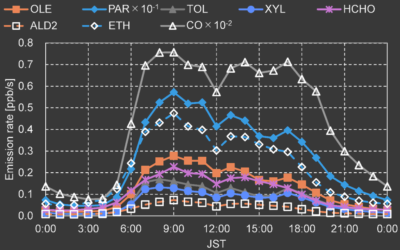
Development and analysis of the inventory of atmospheric pollutant emissions in Panama City
IDDS22-43, funded by SENACYT.
Develop the emissions inventory and analyze their contribution to ambient air pollution in Panama City.
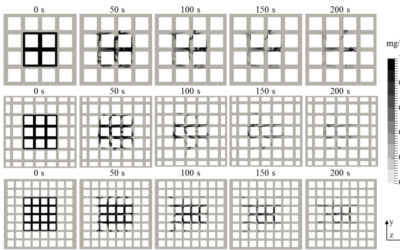
Numerical estimation of pedestrian exposure to pollution caused by vehicular traffic
FIED22-12, funded by SENACYT.
To numerically estimate the exposure of people to environmental pollution caused by internal combustion vehicles, using computational fluid dynamics (CFD).
Determination of vertical profiles of atmospheric pollutants using unmanned aerial vehicles (E-drone)
APY-NI-2022-46, funded by SENACYT.
Determining the vertical profile of atmospheric pollutants using unmanned aerial vehicles.
System for estimating atmospheric emissions from ships INEMIS-SEA
MOV-2023-34, funded by SENACYT.
Estimate atmospheric emissions generated by vessels located around the Pacific side of the Panama Canal.
Our Publications
Estimation of on-road mobile emissions based on the vehicle technology in a high-traffic avenue in Panama City, Panama
Photo by Panama Tribune - News From the Center of the Americas. By: Valdes-Montenegro, A., Gonzalez-Olivardia, F., Thepanondh, S., Pinzon-Acosta, C. Abstract This study addresses the emissions from mobile sources in a busy avenue. Latest mobile emission...
Computational Fluid Dynamics Models to Estimate Pedestrian Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Review
By: Rodriguez-Camarena, C.; Gonzalez-Olivardia, F. Abstract In recent years, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) has become a method widely used by the scientific community to study the dispersion of air pollutants in urban areas. This article analyzes the...
Natural Ventilation Assessment using Computational Fluids Dynamics to Improve Air Quality in Urban Areas
By: Gonzalez Olivardia, Giselle Franchesca Abstract Urban areas represent a major environmental challenge because the air quality degradation in urban environments could impact a great part of the global population. The dispersion of air pollutants in urban areas is...
Impacts of the Tree Canopy and Chemical Reactions on the Dispersion of Reactive Pollutants in Street Canyons
By: Gonzalez Olivardia, F.G.; Matsuo, T.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A. Abstract Traffic-related air pollution in street canyons can cause health problems for pedestrians. In order to clarify the behavior of reactive pollutants, such as NOx and O3, in street canyons, a...
Analysis of Pollutant Dispersion in a Realistic Urban Street Canyon Using Coupled CFD and Chemical Reaction Modeling
By: Gonzalez Olivardia, F.G.; Zhang, Q.; Matsuo, T.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A. Abstract Studies in actual urban settings that integrate chemical reaction modeling, radiation, and particular emissions are mandatory to evaluate the effects of traffic-related air...
Evaluating the Use of Ventilation Efficiency Indices to Improve Urban Ventilation
By: Gonzalez, F., Matsuo, T., Shimadera, H., & Kondo, A. Abstract Removing heated or polluted air is one of the most difficult tasks to accomplish when it comes to ventilating urban environments. This study is an effort to satisfactorily describe the ventilation...
Systematic analysis between ventilation efficiency and building configurations using local age of air
By: Gonzalez, F., Matsuo, T., Shimadera, H., & Kondo, A. Abstract This study aims to show the suitability of the local age of air as a parameter to determine ventilation efficiency. The results have shown that the ventilation efficiency is lower in dense urban...
Use of local age of air to study the relation between ventilation efficiency and building configuration
By: Gonzalez-Olivardia, Matsuo, T., Shimadera, H., & Kondo, A. Abstract Since human population living in urban areas has been increasing rapidly, strategies to reduce the urban heat island effect are becoming more crucial. It is well-known that appropriate...