By: Gonzalez Olivardia, Giselle Franchesca
Abstract
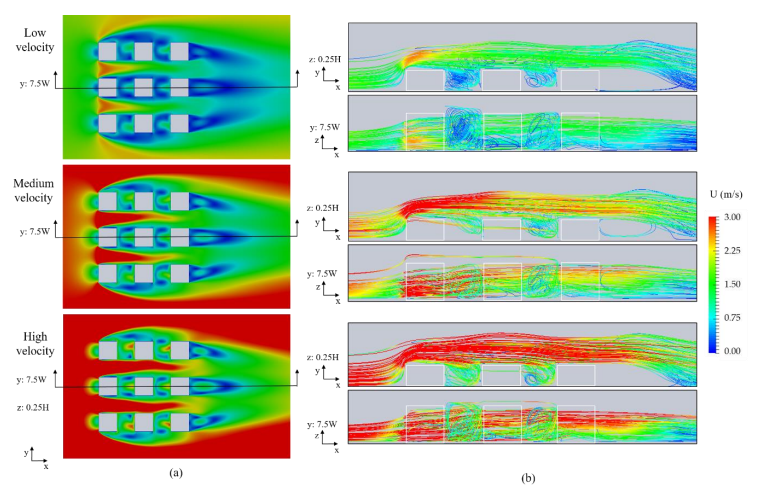
Urban areas represent a major environmental challenge because the air quality degradation in urban environments could impact a great part of the global population. The dispersion of air pollutants in urban areas is conditioned by the interaction of three main factors: the pollution sources, the urban form and components, and meteorological variables. Appropriate quantitively and qualitatively assessment of these interactions will allow better urban planning practices to reduce air pollution in cities. In the second chapter of this doctoral dissertation, a review about urban modeling scales, urban geometries types, and mathematical formulation to numerically model urban areas using Computational Fluids Dynamics
(CFD) is presented. The third chapter presents a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the interaction between meteorological variables and the urban form and components… See complete abstract (PDF)
(CFD) is presented. The third chapter presents a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the interaction between meteorological variables and the urban form and components… See complete abstract (PDF)
Doctoral Thesis / Graduate School of Engineering / 2020. Osaka University, Japan.